Example of Tertiary Structure of Protein
The secondary structure is determined by the dihedral angles of the peptide bonds the tertiary structure by the folding of protein chains in space. Example tertiary structures and.
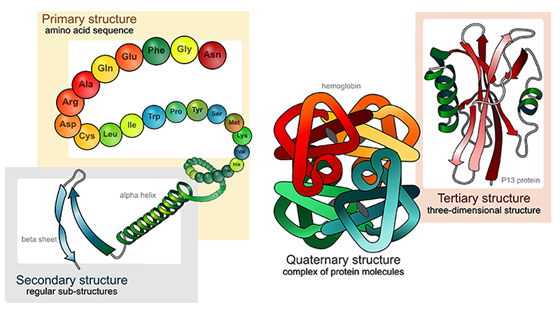
Four Types Of Protein Structure Primary Secondary Tertiary Quaternary Structures
The tertiary structure of a protein refers to the arrangement of amino acid side chains in the protein.

. Protein structure prediction is the inference of the three-dimensional structure of a protein from its amino acid sequencethat is the prediction of its. The sequence of amino acids in a protein is called its primary structure. Tertiary structure is built up from various combinations of secondary structural features.
Th e tertiary structure is the overall three-dimensional shape of a protein. 2 A multimeric protein. The tertiary structure of proteins is maintained by different types of cova-lent and noncovalent interactions.
Tertiary structure is the complete three-dimensional arrangement of all the atoms in a protein. Denatured enzymes lose their catalytic power denatured antibodies can no longer bind antigen A mutation in the gene encoding a protein is a frequent cause of altered. Topology diagrams and motifs.
The tertiary structure of a protein is formed as a result of interaction side chains R-group of amino acids. The interactions and bonds of side chains within a particular protein determine its tertiary structure. All 4 subunits are linked together via hydrogen.
Amino acid side chains may interact and bond in a number of ways. Tertiary Structure refers to the comprehensive 3-D structure of the polypeptide chain of a proteinThere are several types of bonds and forces that hold a protein in its tertiary structure. There are in all twenty amino acids in the human body.
Protein tertiary structure is the three dimensional shape of a proteinThe tertiary structure will have a single polypeptide chain backbone with one or more protein secondary structures the protein domains. Ad Products empowering scientists at every stage helping to deliver scientific breakthroughs. The overall three-dimensional arrangement of all atoms in a protein.
Generally the information for protein structure is contained within the amino acid sequence of the protein itself. Th e tertiary structure of enzymes. If this is disrupted the protein is said to be denatured and it loses its activity.
Constituent amino-acids can be analyzed to predict secondary tertiary and quaternary protein structure. 3 A globular domain. Leading life science supplier for your research development or production needs.
23 The tertiary structure of proteins. An example of this structure of a protein is hemoglobin Hb. The function of a protein except as food depends on its tertiary structure.
Which of the following is an example of tertiary structure in a protein. Quaternary Structure of Protein. Hydrophobic interactions greatly contribute to the folding and shaping of a proteinThe R group of the amino acid is either hydrophobic or hydrophilic.
Tertiary structure is the overall conformation and resulting three-dimensional shape of a polypeptide chain. Protein structures are made by condensation of amino acids forming peptide bonds. Proteins adopt various tertiary structures ultimately based upon primary structure.
TERTIARY STRUCTURE OF PROTEINS Tertiary Structure describes the shapes which form when the secondary spirals of the protein chain further fold up on themselves. Protein gets all its properties from its primary structure. All of these have a carboxyl group and an amino group.
This important principle of biochemistry was first determined by the biochemist Christian Anfinsen in studies of the enzyme. Folding of the peptide chain within a domain usually occurs independentlay of folding in others domain. Each Hb molecule has 4 peptide chains 2 α-chains and 2 β-chains forming a tetramer.
Structural proteins are quite ordered in shape whereas globular proteins such as enzymes and receptors Chapters 3 and 4 fold up to form more complex structures. The primary structure is the unique formation and order in which the amino acids the building blocks combine and link to give us a protein molecule. 4 A P-pleated sheet.
Hydrogen bonding occurs between atoms on the peptide backbone as well as atoms in the side chains.
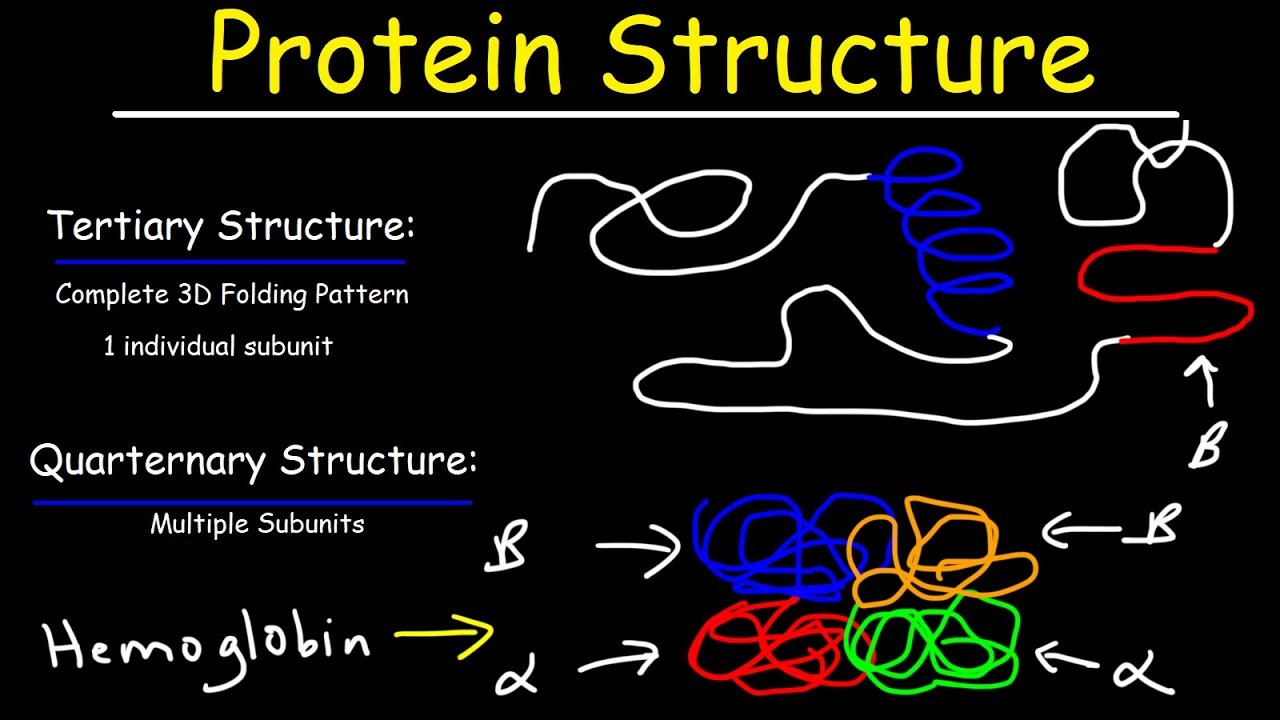
Protein Structure Primary Secondary Tertiary Quarternary Biology Youtube
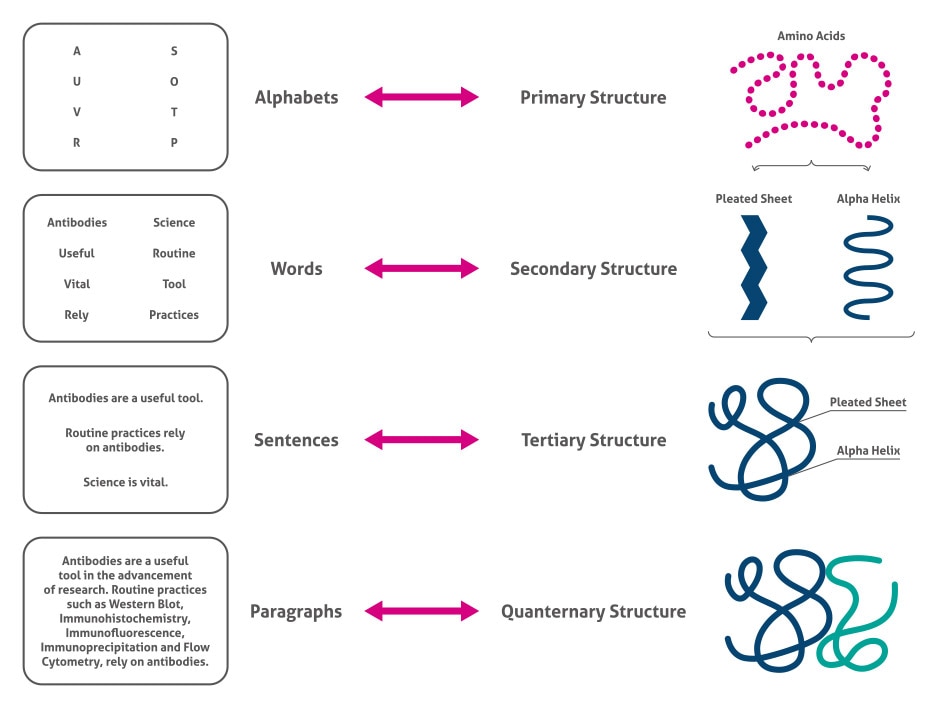
The Complexity Of Proteins Proteintech Group

Tertiary Structure Protein Structure Tutorials Msoe Center For Biomolecular Modeling

No comments for "Example of Tertiary Structure of Protein"
Post a Comment